ABSTRACT
Hand sign detection is an important concept for helping the challenged communicate. The project deals with the mentioned problem and uses deep connected neural networks for detection of hand signs and recognition of English alphabets. The wide spread of American Sign Language(ASL) was used for detection. Mediapipe framework was used for recognizing and extracting the keypoints through real time hand detection and saved in csv files which were fed to neural network for training. pandas and other libraries have facilitated in operating and utilising the collected data. Non linear activation functions such as ReLu, tanh have used in combination with softmax at its final layer. Through the results obtained we have finalised that Data preprocessing plays in important role in model learning capabilities. Batch normalization has yielded better accuracy and prediction when compared with models that are not batch normalized.
INTRODUCTION
Mediapipe is an open-source framework developed by google. The framework allows to capture the keypoints and landmarks of several parts of human body such as face, hand, body. In this project we mainly discuss on capturing keypoints and landmarks from the hands in real-time. Mediapipe has several in-built methods to extract the key points. The framework accesses the user webcam and with a custom function written, it extracts the landmarks from user`s hands with just a key press on keyboard. This method was followed to collect data for 26 English alphabets from both left and right hands. The framework also helps in saving storage space and training time as it directly extracts the landmarks into file without the need to store the images. A second method involving static images to extract the landmarks was also used. Where the kaggle dataset on ASL alphabets was fed into a custom method written using mediapipe which extracts the landmarks.
METHOD
Dataset
Manually collected dataset was preferred over the kaggle dataset
Models
Eight models in total were used to compare the performances and impacts of using different regularizations, dropout, batch normalization configurations. The basic structure of all the models have a tensor of size 42 as input [each tensor indicating the x and y coordinates of individual keypoints], five dense layers for which each of them having tanh or ReLu as an activation function except the final output layer configured with softmax as activation function. the initial dense layer having 512 as the output for the consequent layer and gradually decreasing the output values to number of alphabets i.e 26. All the models have default batch size of 128 and 300 epochs for training
Base Model
As the name suggests this is the base model with no regularization, dropout, batch normalization. This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and has four subsequent dense layers each having tanh as their activation function and the final output layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This model has sigmoid as it’s optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation
Model with L1 Regularizer [Model 1]
The effect of L1 regularization on neural networks is to decrease the complexity of the model by reducing the number of weights and biases. L1 regularization is a technique used to prevent overfitting in neural networks. It does this by adding a penalty term to the cost function during training that is proportional to the sum of the absolute values of the weights and biases in the network. This penalty term encourages the network to reduce the number of weights and biases that are used to make predictions, which can help to prevent overfitting and improve the generalizability of the model. As a result, L1 regularization can improve the performance of neural networks on unseen data. This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and has four subsequent dense layers each having tanh as their activation function, where the first dense layer is configured with L1 regularizer and the final output layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This model has sigmoid as it’s optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation
Model with L1 Regularizer in all dense layers [Model 2]
This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and has four subsequent dense layers each having tanh as their activation function and L1 regularization applied, the final output layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This model has sigmoid as it’s optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation
Model with L2 Regularizer [Model 3]
As seen earlier, L1 regularization penalizes the sum of absolute values of the weights, whereas L2 regularization penalizes the sum of squares of the weights. This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and has four subsequent dense layers each having ReLu as their activation function, where the first dense layer is configured with L2 regularizer and the final output layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This model has adam optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation
Model with L2 Regularizer in all dense layers [Model 4]
This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and has four s ubsequent dense layers each having tanh as their activation function and L2 regularization applied, dense layer before the ouput layer having ReLu as activation function the final output layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This model has adam optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation
Model with a single layer of 50% dropout rate [Model 5]
Dropout is a regularization technique used to reduce overfitting in a neural network. It works by randomly dropping out, or setting to zero, a certain number of neurons in the network during training. This has the effect of forcing the network to learn multiple independent representations of the data, which can help prevent the network from overfitting to the training data. This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and has a dropout layer and four dense layers each having tanh as their activation function, dense layer before the ouput layer having ReLu as activation function the final output layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This model has adam optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation.
Model with multiple dropout layers [Model 6]
This model consists of multiple dropout layers with varying rates.It has four dropout layers out of which the first three have 50% dropout rate and the last one has 30% dropout rate. Apart from this model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and four dense layers each having tanh as their activation function, dense layer before the ouput layer having ReLu as activation function the final output layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This model has adam optimizer and sparse categorical c rossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation.
Model with Batch Normalization [Model 7]
Batch normalization is a technique used to improve the performance and stability of neural networks. It works by normalizing the inputs to a layer in a neural network, which can help the network learn faster and reduce the amount of vanishing or exploding gradients. This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and four dense layers each having tanh as their activation function,a batch normalization layer, the final output lay er having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. This mode l has adam optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the e valuation metrics during model training and evaluation.
Model with multiple Batch Normalization layers [Model 8]
This model consists of an input which takes a tensor of size 42 as an input and four dense layer search having tanh as their activation function,a batch normalization layer after each dense layer, the final outp ut layer having softmax as its activation function with 26 output values each indicating the individual english alphabets. Thi s model has adam optimizer and sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss function and accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error] as the evaluation metrics during model training and evaluation.
Evaluation metrics
Each model has the same evaluation metrics. Accuracy and MSE[Mean Squared Error]
Accuracy
Accuracy is a metric that is used to evaluate the performance of a machine learning model. It is the percentage of correct predictions that the model makes on a dataset. This can be done by comparing the predicted values wit h the ground truth or true values. The number of correct predictions is then divided by the total number of predictions, and the resu lt is multiplied by 100 to obtain the accuracy as a percentage.
ACCURACY = TOTAL NO OF CORRECT PREDICTIONS / TOTAL NO OF PREDICTIONS
Mean Squared Error
Mean squared error (MSE) is a measure of the average squared difference between the predicted and actual values of a data set. It is often used as a metric to evaluate the performance of a machine learning model.
MSE = 1⁄n Σ(yi − pi)2
where yi is the ith observed value, pi is the corresponding predicted value for yi, and n is the number of observations. The Σ indicates that a summation is performed over all values of i
RESULTS
Analysis and discussion
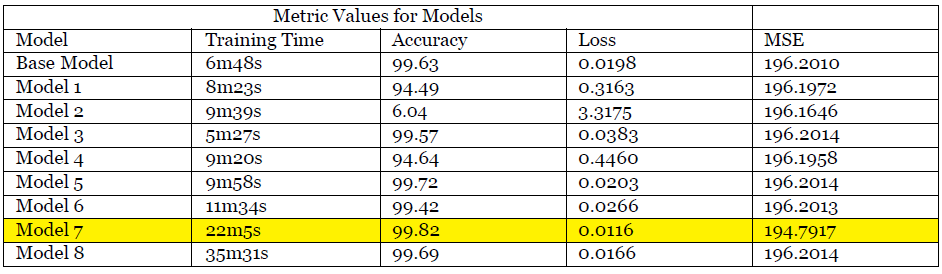
- + When comparing Model 1 and Model 2, Model 1 performs better because too much regularization can also hinder the performance of the network by limiting its ability to capture important patterns in the data. And also if you observe Model 2’s performance drastically reduces because of over regularization.
- + When Comparing Model 3 and Model 4, Model 3 performs better because of the reason similar to in the earlier point.
- + When comparing Model 5 and Model 6, Model 5 performs better because dropout is introduced to reduce the overfitting of the model by generalization. But too many layers can also lead to dropping important features in data.
- + When comparing Model 7 and Model 8, Model 7 performs better because too many batch normalization layers can also hinder the performance of the network by introducing unnecessary computational overhead and limiting its ability to capture complex patterns in the data. It is clear that by looking at the time taken to train Model 8 is almost 60% longer then Model 7.
CONCLUSION
To summarize, the dataset was manually collected with the help of code written using mediapipe framework. Nine different models were created to show the effect of Regularization, dropout, Batch Normalization and it’s extreme cases and how training time does not have any impact on model’s accuracy. The model’s accuracy depends on the architecture of the network which is clear when we look at the results of multiple models that were trained, Model 7 i.e the model with single batch normalization layer was the best performing model . Below are the predictions given by the Model 7 in real-time :